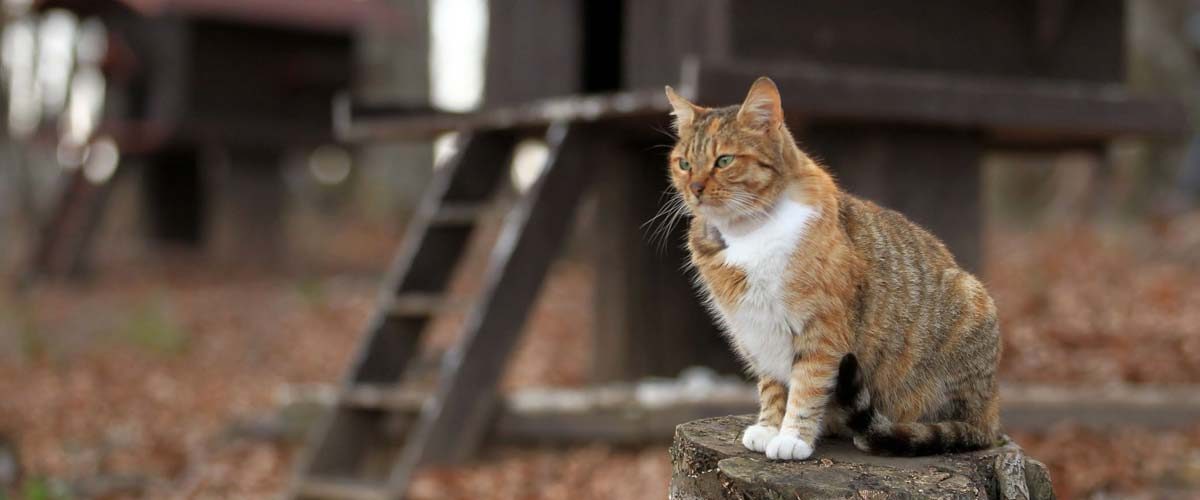
Toxoplasmosis is a protozoal infection that spreads commonly among warm blood species across the world. One of the study published in The Journal of Infection in Developing Countries, pointed out the rise of Toxoplasma gondii infection in Turkey. It was for the first time, the scientist correlated a spread of infection through stray cats feces.
The lead author, MuhammetKarakavuk identified that the prevalence of toxoplasmosis was fairly high among the residents and animals of Izmir. According to medical literature, this protozoan is commonly found in mammals and birds, which disseminates the infection through feces. Likewise, the research team attested, “the transmission of ingested oocyst occurs mainly occurred through the stray cat’s feces, which was proven after sampling the feces of 465 stray cats.”
The love for pets and close proximity with them harbors some associated risks among the residents in various places. Even the ingestion of uncooked meat is a major factor for transmission. It has been reported, “ millions of oocyst are shed through cats feces each day with seroprevalence ranging from 30 to 40% among them.”
The team analyzed the feces using microscopy that revealed oocysts presence in 0.43% of cats whereas T. gondii DNA was identified in 14.37% of the stray cats’ feces. Furthermore, to test the immunity of these cats against the infection, their blood samples were drawn, which revealed a 37.84% seroprevalence rate with 35.89% seropositive cats.
Thus, the author concluded, “the prevalence of high infection among the cats proves to be contagious for other animals and humans as well. Moreover, the high seroprevalence among the birds (90%) can also act as a source for transmission to non-infected cats. Hence, people should refrain from interacting with stray cats and constant monitoring is necessary to control the spread of toxoplasmosis.












Add comment