We started working on the issue of developing a readily available testing method as soon as we saw the developments in Asia and southern Europe, and before the situation reached crisis point in Sweden,” says principal investigator Bjorn Reinius, research leader at the Department of Medical Biochemistry and Biophysics at Karolinska Institutet. “Our method was effectively finished already by the end of April, and we then made all the data freely available online.
The spread of the new coronavirus at the end of 2019 in China’s Wuhan region quickly escalated into a global pandemic. The relatively high transmission rate and a large number of asymptomatic infections led to a vast, worldwide need for fast, affordable, and effective diagnostic tests that could be performed in clinical as well as non-clinical settings.
Established diagnostic tests for COVID-19 are based on detecting viral RNA in patient samples, such as nasal and throat swabs, from which RNA molecules must then be extracted and purified. RNA purification constitutes a significant bottleneck for the testing process, requiring many equipment and logistics and expensive chemical compounds.
Making the current methods more straightforward without markedly compromising their accuracy means that more and faster testing can be carried out, which would reduce the rate of transmission and facilitate earlier-stage care.
The cross-departmental research group at Karolinska Institutet has now developed methods that circumvent the RNA-extraction procedure entirely. Once the patient sample has been inactivated by means of heating, rendering the virus particles no longer infectious, it can pass straight to the diagnostic reaction that detects the presence of the virus.
According to the researchers, the most important keys to the method’s success are both the above virus inactivation procedure and a new formulation of the solution used to collect and transport the sample material taken from the patients.
By replacing the collection buffer with simple and inexpensive buffer formulations, we can enable viral detection with high sensitivity directly from the original clinical sample, without any intermediate steps, says Dr. Reinius.
Institutions and research groups worldwide have shown great interest in the method since the first version of the scientific article was published on the preprint server medRxiv. The report was read more than 15,000 times even before it was peer-reviewed by other researchers in the field and officially published in Nature Communications.
“Thanks to the low cost and the simplicity of the method, it becomes a particularly attractive option at sites and in situations with limited resources but a pressing need to test for COVID-19,” he says and adds: “I would certainly like to see that this test used in Sweden too, for example for cheap periodic testing of asymptomatic people to eliminate the spread of infection.”
The study was supported by grants from the Wallenberg Foundations via the SciLifeLab/KAW National COVID-19 Research Program and from the Ragnar Soderberg Foundation.
Source: Karolinska Institutet
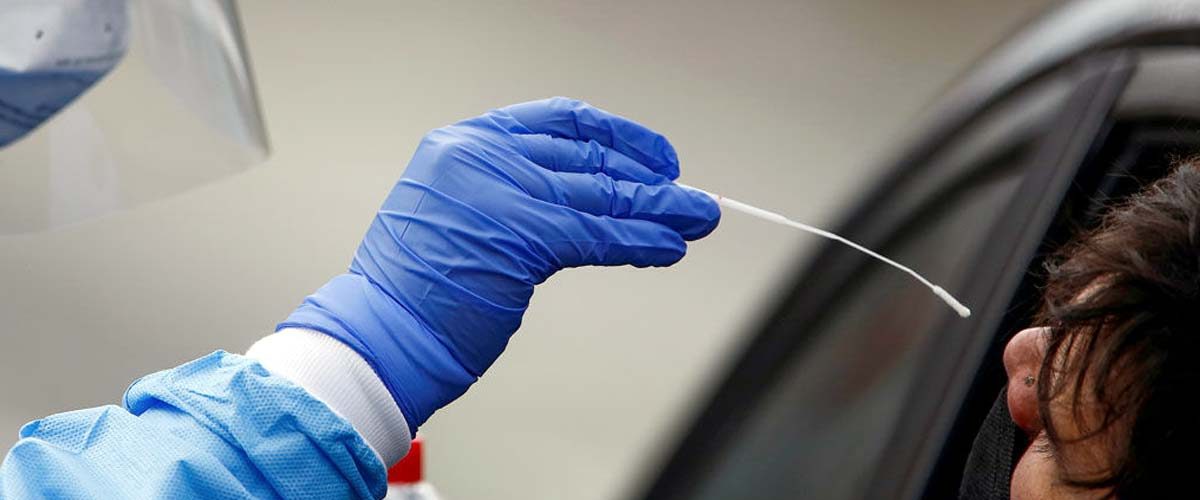












During the current pandemic when the world is facing limited economic growth rapid, cheaper and simple testing methods will help to overcome the situation and in this regard, the study is very helpful for lab analysts.
Much needed study
Especially In Pakistan where the economic growth is already facing a huge downfall.These simple and cheaper testing methods would help the country to overcome this pandemic.